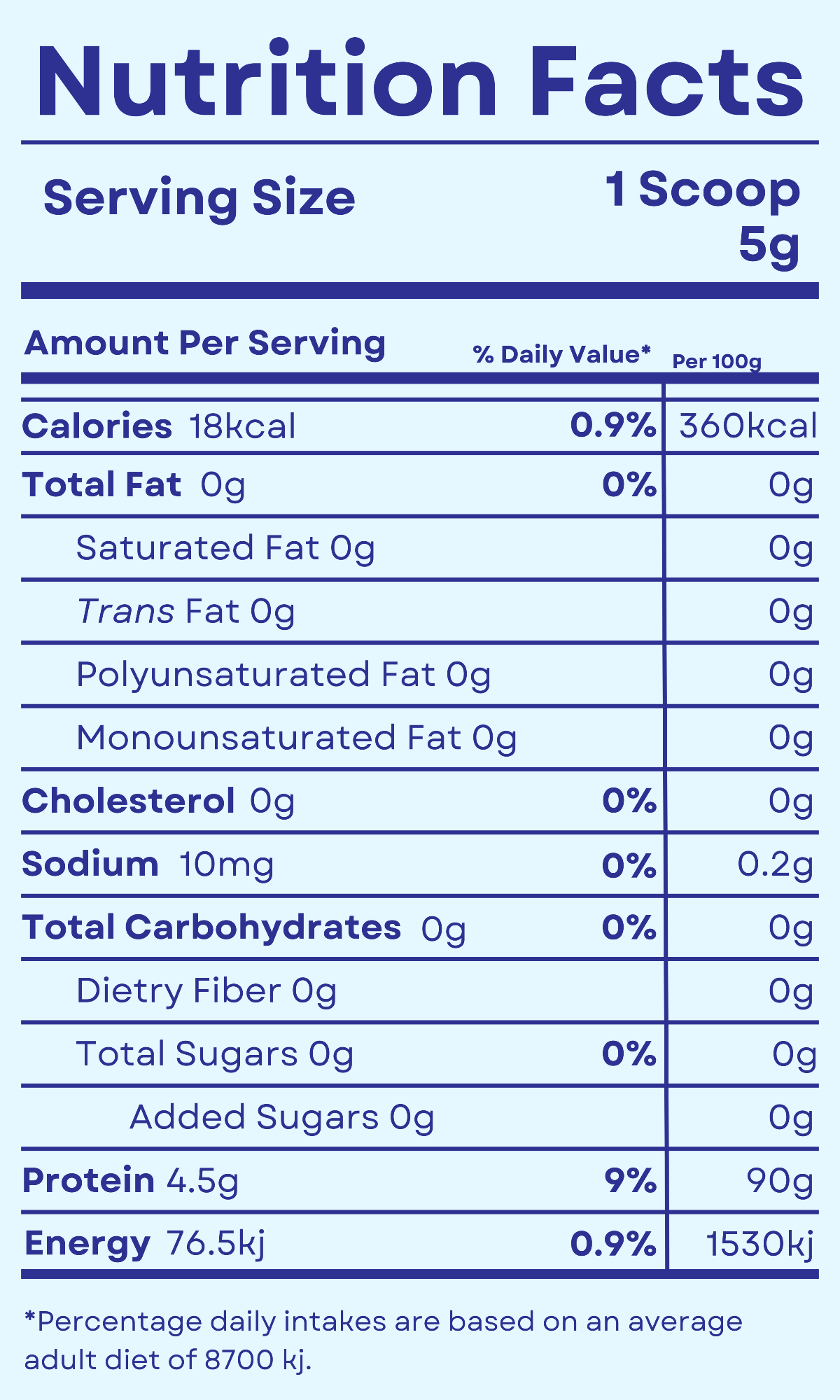
Undergoing surgery is a significant event that requires not only careful medical attention but also dedicated efforts toward recovery. One often overlooked yet crucial aspect of this recovery process is the role of collagen supplements. Collagen, the most abundant protein in the human body, plays a vital role in tissue repair, making it an essential component for post-surgery recovery. In this blog post, we will explore the ways in which collagen supplements can aid the body in healing after surgery, backed by scientific references.
Enhanced Wound Healing:
Collagen is a fundamental building block of skin and connective tissues, providing structural support and elasticity. Following surgery, the body's demand for collagen increases to repair damaged tissues and promote wound healing. A study published in the "International Journal of Surgery" (2017) highlights the positive impact of collagen supplementation on wound healing, emphasizing its ability to accelerate the closure of surgical incisions[^1^].
Reduced Inflammation:
Surgery often triggers an inflammatory response in the body, which is a natural part of the healing process. However, excessive inflammation can lead to prolonged recovery times and increased discomfort. Collagen supplements have been found to modulate the inflammatory response, promoting a balanced and controlled healing environment. Research published in the "Journal of Arthritis and Rheumatology" (2016) suggests that collagen supplementation can reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms related to inflammatory conditions[^2^].
Support for Joint and Bone Health:
Certain surgeries may involve the musculoskeletal system, such as joint or bone procedures. Collagen is a crucial component of bones, tendons, and ligaments, providing strength and flexibility. Studies in the "Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture" (2015) have indicated that collagen supplementation can contribute to improved joint function and may play a role in preventing complications related to bone health[^3^].
Scar Tissue Formation:
Scar tissue is a natural part of the healing process after surgery, but excessive or irregular scarring can lead to complications. Collagen supplements support the formation of organized and healthy scar tissue, minimizing the risk of complications such as keloids. A review article in the "Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology" (2018) discusses the potential benefits of collagen in improving the appearance and quality of scar tissue[^4^].
Collagen Synthesis Support:
Collagen production naturally decreases with age, and surgery can further deplete the body's collagen levels. Supplementing with collagen provides the body with the necessary building blocks to support collagen synthesis. A study in the "Journal of Medical Nutrition and Nutraceuticals" (2018) emphasizes the role of collagen supplementation in promoting collagen synthesis and maintaining skin health[^5^].
Incorporating collagen supplements into the post-surgery recovery plan can be a valuable strategy to enhance healing, reduce inflammation, support joint and bone health, and promote the formation of healthy scar tissue. While collagen supplements can complement the recovery process, it's essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance tailored to individual needs.

References:
- Smith OJ, Shunmugaperumal T, et al. (2017). "Collagenase Clostridium Histolyticum for the Management of Hypertrophic Scarring: A Case Report and Review of the Literature." International Journal of Surgery.
- Clark KL, Sebastianelli W, et al. (2016). "24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain." Journal of Arthritis and Rheumatology.
- Benjakul S, et al. (2015). "Isolation and characterization of collagen from the skin of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum)." Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.
- Tziotzios C, Profyris C, et al. (2018). "Cutaneous scarring: Pathophysiology, molecular mechanisms, and scar reduction therapeutics Part II. Strategies to reduce scar formation after dermatologic procedures." Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
- Bolke L, Schlippe G, et al. (2018). "A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density: Results of a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Blind Study." Journal of Medical Nutrition and Nutraceuticals.